Brain Haemorrhage – Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
Brain Haemorrhage – Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentInformation by Turkish Neurosurgeon in London, Dr Ufuk Soylu
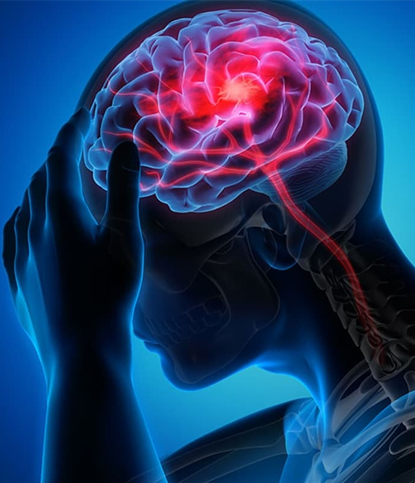
A brain haemorrhage (also known as a brain bleed) occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures, causing blood to leak into or around the brain tissue. This leads to pressure on the brain, interrupting its normal function and potentially resulting in serious or life-threatening complications.
Among the Turkish community living in the UK, high blood pressure, stress, and lifestyle factors are common causes of brain vascular problems. Recognising the early signs and seeking immediate medical attention can be life-saving.
🔹 Types of Brain Haemorrhage
Brain haemorrhages are classified according to where the bleeding occurs:
• Intracerebral haemorrhage: Bleeding inside the brain tissue itself.
• Subarachnoid haemorrhage: Bleeding between the brain and its surrounding membranes, usually caused by a ruptured aneurysm.
• Subdural / Epidural haemorrhage: Often caused by head injuries or trauma.
All types require urgent medical assessment and treatment.
🔹 Causes of Brain Haemorrhage
The most common cause is uncontrolled high blood pressure (hypertension), which weakens blood vessel walls over time and increases the risk of rupture.
Other causes include:
• Head trauma or accidents
• Aneurysm (a bulging or weakened artery)
• Overuse of blood-thinning medications
• Vascular malformations (AVMs)
• Blood clotting disorders
🔹 Symptoms of Brain Haemorrhage
Symptoms often appear suddenly and can be severe.
If you notice any of the signs below, call 999 immediately or go to the nearest emergency department:
• Sudden, severe headache ("the worst headache of my life")
• Nausea or vomiting
• Loss of consciousness or confusion
• Weakness or numbness on one side of the body
• Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
• Vision problems or double vision
• Loss of balance or coordination
Even one of these symptoms can indicate a serious brain bleed.
🔹 Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made through CT (Computed Tomography) or MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scans.
These imaging methods help determine the location and severity of bleeding.
In some cases, cerebral angiography (DSA) is used to identify aneurysms or vascular malformations.
🔹 Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the type, cause, and severity of the haemorrhage.
• Surgical treatment: To remove blood clots, relieve pressure, or repair a ruptured aneurysm.
• Medical management: To control blood pressure, reduce brain swelling, and prevent further bleeding.
Early and accurate intervention greatly improves the chances of recovery.
🔹 Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery after a brain haemorrhage can take time. It depends on the patient's overall health, age, and the location of the bleeding.
Rehabilitation may include physiotherapy, speech therapy, and neurological rehabilitation to help patients regain independence and daily function.
🔹 Preventing Brain Haemorrhage
While not all cases can be prevented, certain steps can reduce the risk:
• Monitor and control your blood pressure regularly
• Eat a balanced diet and reduce salt intake
• Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol
• Manage stress effectively
• Use seatbelts and helmets to prevent head injuries
🧠 Dr Ufuk Soylu – Turkish Neurosurgeon in London
As a specialist in brain and spine surgery, I provide diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up care for brain haemorrhages and other neurological conditions.
If you or someone close to you experiences symptoms of a brain bleed, seek emergency help immediately. Early intervention can save lives and improve long-term outcomes.